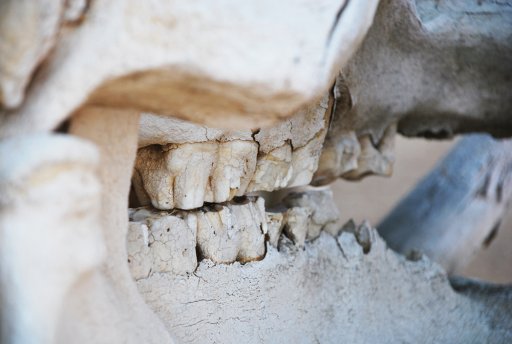
Jenny McGuire will study Africa's fossil record to inform conservation biology decisions and forecast how humans and climate affect wildlife — building a better understanding between animals, physical traits over time, response to environmental changes.
Jenny McGuire will study Africa's fossil record to inform conservation biology decisions and forecast how humans and climate affect wildlife — building a better understanding between animals, physical traits over time, response to environmental changes.
Jenny McGuire will study Africa's fossil record to inform conservation biology decisions and forecast how humans and climate affect wildlife — building a better understanding between animals, physical traits over time, response to environmental changes.
Jenny McGuire will study Africa's fossil record to inform conservation biology decisions and forecast how humans and climate affect wildlife — building a better understanding between animals, physical traits over time, response to environmental changes.
Jenny McGuire will study Africa's fossil record to inform conservation biology decisions and forecast how humans and climate affect wildlife — building a better understanding between animals, physical traits over time, response to environmental changes.
As of this week, the omicron variant makes up the majority of new coronavirus cases in the U.S.
Minda Monteagudo is a one-of-a-kind student, literally. She is the first student to ever graduate with a Ph.D. in ocean sciences and engineering from Georgia Tech.
Georgia Tech scientists and engineers are building a new DOE-funded instrument that captures 3D images of plant-microbe chemical reactions underground in an interdisciplinary effort to develop biofuels and fertilizers — and help mitigate climate change.
Georgia Tech scientists and engineers are building a new DOE-funded instrument that captures 3D images of plant-microbe chemical reactions underground in an interdisciplinary effort to develop biofuels and fertilizers — and help mitigate climate change.
Georgia Tech scientists and engineers are building a new DOE-funded instrument that captures 3D images of plant-microbe chemical reactions underground in an interdisciplinary effort to develop biofuels and fertilizers — and help mitigate climate change.
Pagination
- Previous page
- 46 Page 46
- Next page